|
Tamilnadu
Sharing boundaries with the states of Andhra Pradesh , Karnataka, and Kerala, Tamil Nadu has an unbroken coast line, edging
the Bay of Bengal. Densely forested uplands which abound in wildlife, intensively cultivated farmlands interspersed with rocky
wastes, mountain chains of the Western Ghats which give way to fertile coastal plains and plateaus form the geographical features
of Tamil Nadu. Tamil Nadu is watered by several perennial rain fed rivers and the 760 kilometre long Cauvery travels the entire
breadth of the state.

History
The history of Tamil Nadu dates back to the time, the Dravidians had moved south, following the advent of Aryans in the
north. Historically, South India consisted of four main Dravidian Kingdoms, the Pallavas, the Cholas, the Pandyas (who ruled
over what is now Tamil Nadu) and the Chalukyas. The Muslim invasion of the South in the 14th century, caused a retaliatory
reaction from the Hindus, who rallied to build a strong new kingdom, with its capital at Vijaynagar. On independence, the
Madras province, as the south was known then, was divided on a linguistic basis into states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Andhra
Pradesh.
Culture
Tamilians learn to appreciate culture from a very young age, and have a deep interest in music, dance and literature. Classical
dancing in the form of Bharatnatyam, has its origin in the temples of the South East and continues to be followed with
a lot of fervour and dedication in Tamil Nadu. Carnatic music is another art form, that has flourished over the ages, producing
artists of great repute. A unique festival of Carnatic music, the Thyagaraja festival is held annually in January at Thiruvariyar,
the birth place of famous singer poet Thyagaraja, where one can witness the amazing spectacle of mass performance, in total
harmony and rhythm. Festivals are a daily feature in this region. Navaratri (September/October), Deepavali (October/
November), Karthika (November/December) and Pongal (January ) are the popular ones.

Economy
Agriculture is the mainstay of Tamil Nadu's economy, with the main food crops being rice, pulses and oil seeds. Important
commercial crops that are grown in Tamil Nadu include sugarcane, cotton, tea, rubber, cashew and coconut. Major forest products
are timber, sandalwood, pulpwood and fuel wood, while the minor products include bamboo, eucalyptus, rubber, tea, cashew,
honey and ivory.
Major industries in Tamil Nadu are cotton textiles, chemical fertilizers, paper and its products, printing and allied industries,
diesel engines, automobiles and its ancillaries, bicycles, cement, iron & steel, railway wagons and coaches. The minerals
found in Tamil Nadu are limestone, magnesite, mica, quartz, felspar, salt, bauxite, lignite and gypsum. The state is an important
exporter of tanned skin, hides, leather goods, cotton goods and yarn, tea, coffee, spices, engineering goods, tobacco, handicrafts
and black granite.


Places to Visit
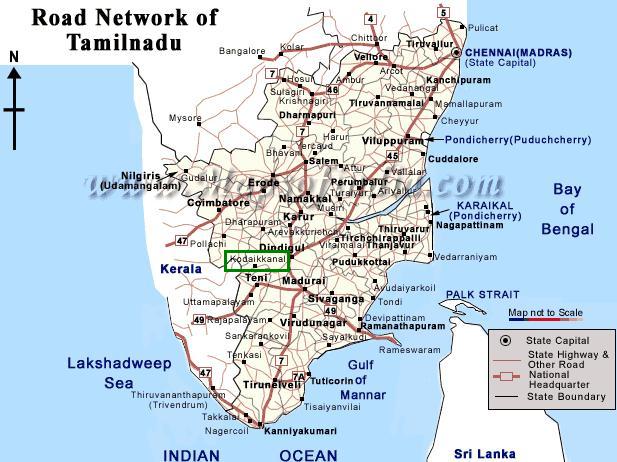
The places of tourist interest in the state are Chennai, the beautiful capital city; Mamallapuram, the beach resort; Kanchipuram,
the land of 1000 temples; Madurai famous for the Meenakshi temple; Rameshwaram, Tiruchirapalli and Thanjavur, the temple
trio; the charming hill resorts of Yercaud, Ootacamund and Kodaikanal and Kanyakumari, the southern tip of India, renowned
for its fantastic sunrise and sunset.
|

